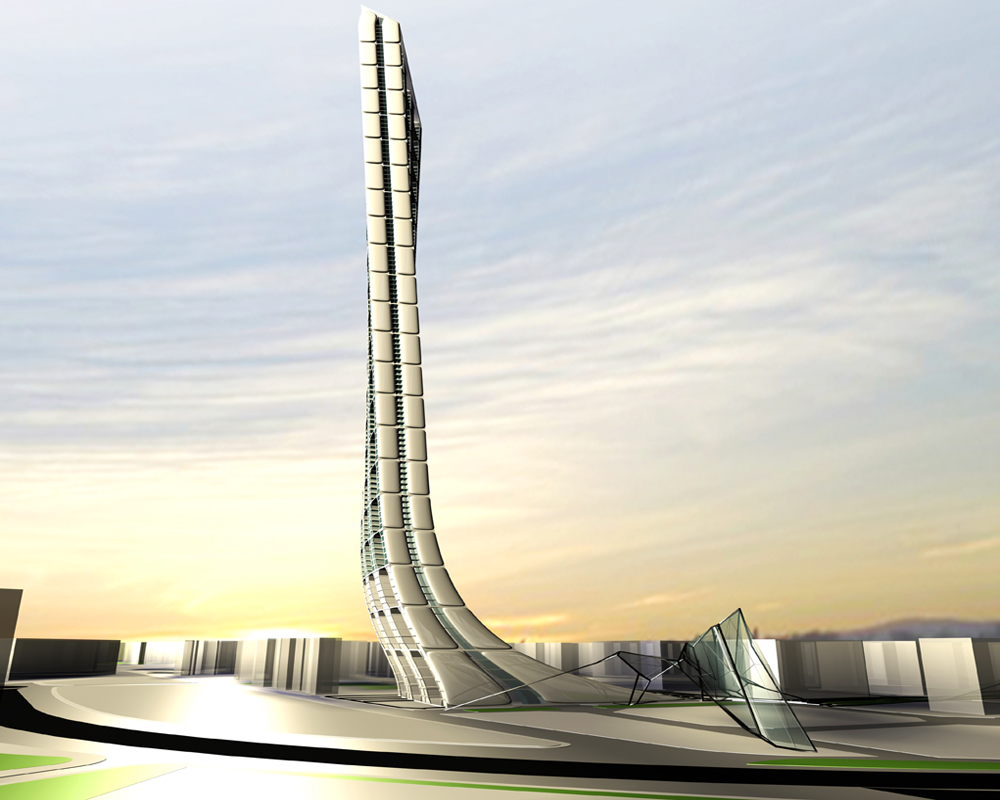
Evolo 09 Skyscraper – Barcelona Infinity
2007
Competition
Arch. Marco De Gregorio
The city/Urban Scenarios
Barcelona is an attractive and commercial city that has become one of the major destination cities of the world. The city has double its population in the last century absorbing both a permanent living population but also tourists, visitors and commuters that lives in the city for a short or a long term .
That makes Barcelona one of the most dense cities in Europe.
In the mid-19th century , the purpose of a new contemporary city was already developed by the “idea of urbanization”
Ildefonso Cerdà was a pioneer of a modern urban planning by his forceful, functional and “democratic” concept of reshaping Barcelona to adhance a better future for the citizens, and to become a new European metropoly.
Cerdà carefully designed the layout of the city expansion called Eixample, breaking down the city walls, and proposing a 60-hectare extension of the city, with 325 plots, mansanas, consisting of 113 meters squared blocks and with 20 meters wide street s. Their guidelines corresponded to the dominant lines of the plain and were oriented at 45° from the north, repeating the roman layout.
The original layout of Cerdà consisted of a the strictly urban organization, a rigorously geometry order that should provide an interior “green” courtyard in each block. The metropolitan plan ensured communal public spaces and local gardens throughout the city, but the densifications of the suburban fabrics made an explosive intensification that unfortunately made the Eixample urban structure area congestive.
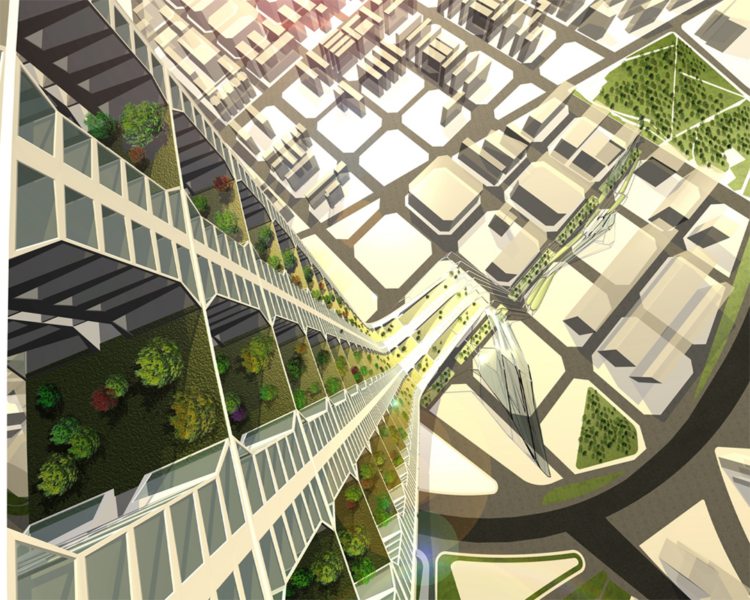
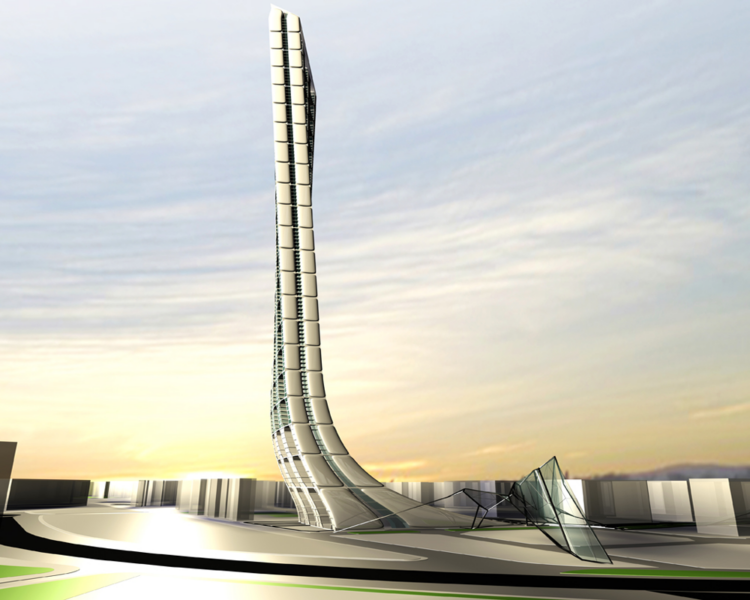
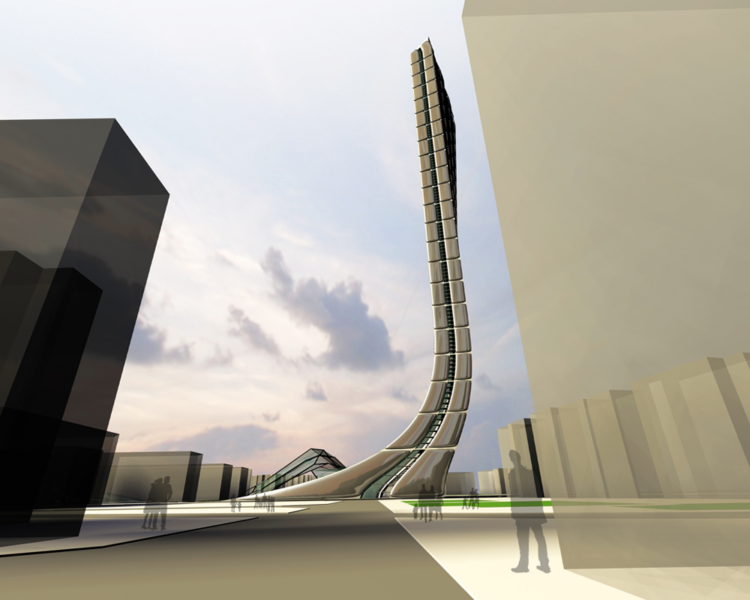
The site of the proposal is situated at the end of the main city axes Avenguida Diagonal at the north close to the coast of Barcelona in el Besos i el Maresme which is today the new expansion area of the city.
Analysis
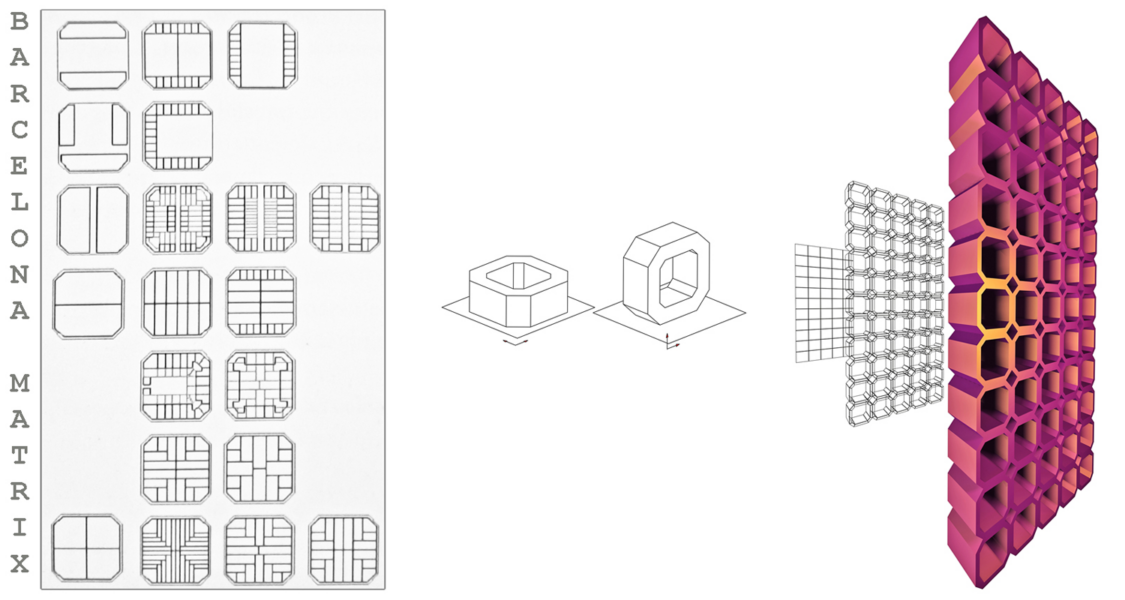
The research is based on the analysis of Cerdà’s grid system and on the study of the socials aspects of the living and the further expansion of Barcelona. The concept is based on the Cerda Eixample plan, developing the parametric form and focuses on the squared housing block, mansana, as a quality space of living.
The urban horizontal Cerdà Matrix becomes a vertical dynamic force.
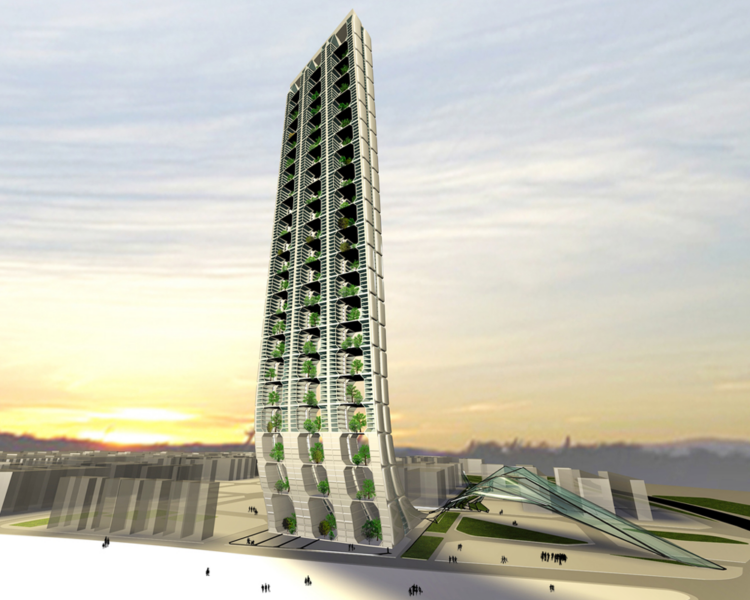
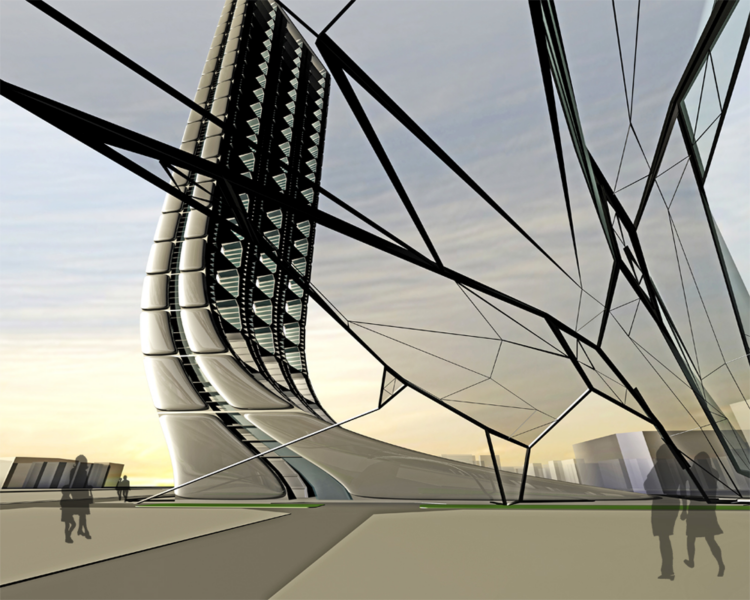
As a continuation of the grid, the building structure becomes a fluid expansion so the density of the territory is analogically translated into a vertical structure, the Skyscraper.
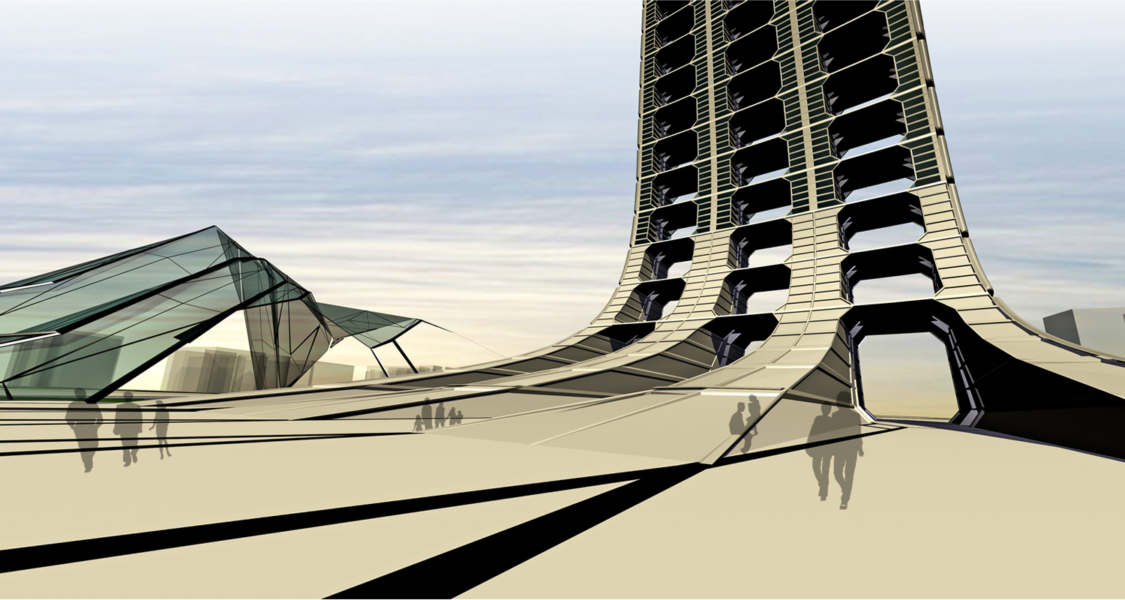
The structure is a multifunctional organization, a spatial layout that provides dynamic forces for social and private enterprizes, from the public use at ground floor to the semi public above and to the residential to.
The Unit/Vertical mansana
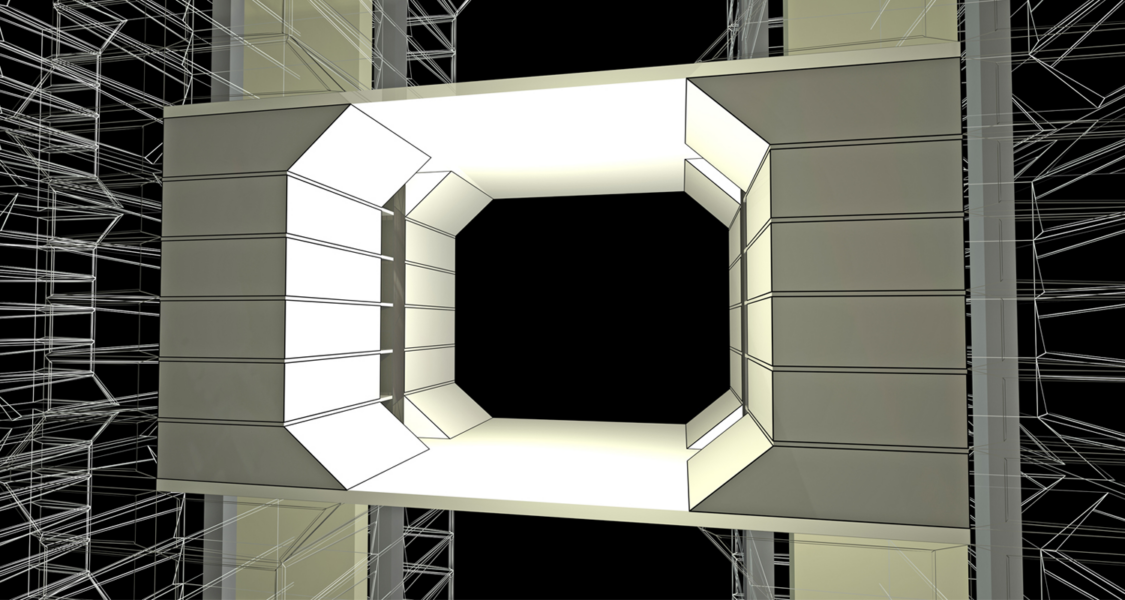
The residential part of the skyscraper consist of 400 housing units and each unit can be considered as an individual community in itself.
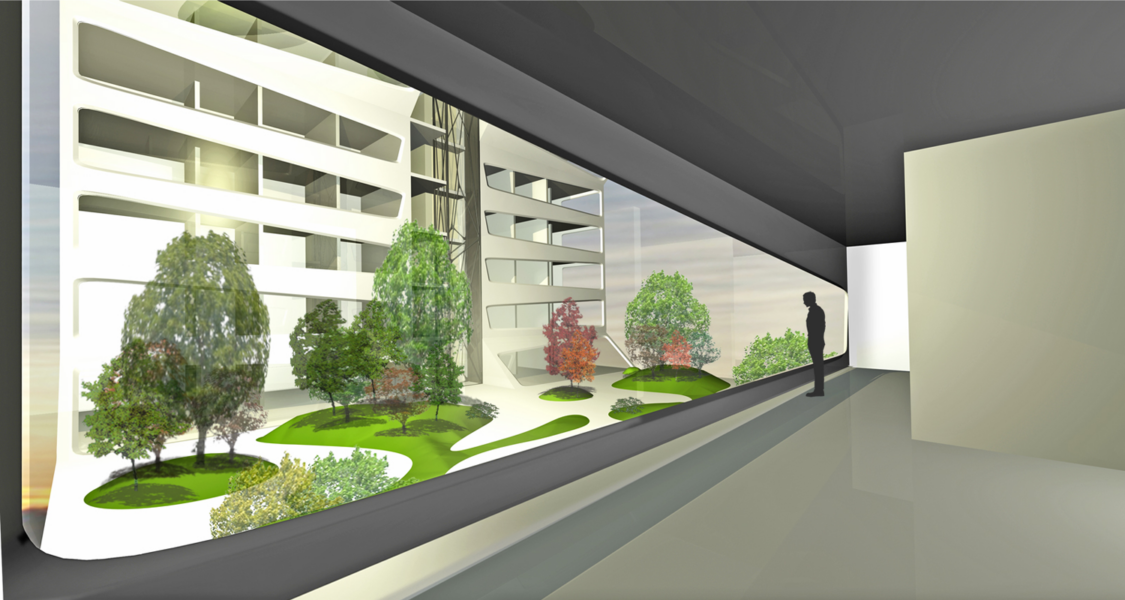
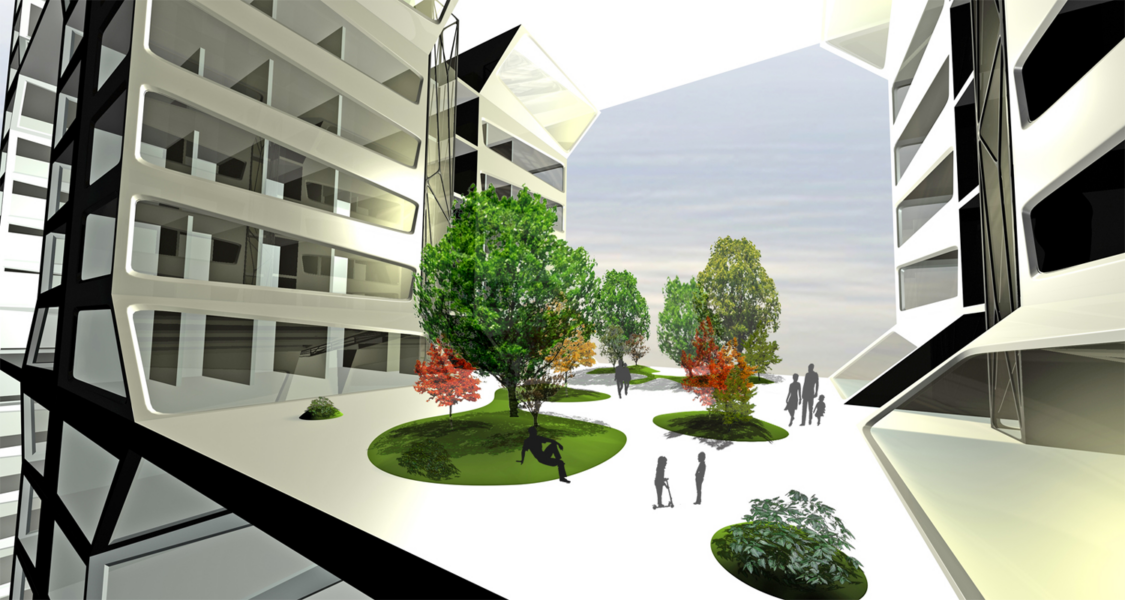
Each Unit consist of 24 flats and they are equally placed around and sharing a communal space, a garden square and a terrace, with trees and plants to compensate for lacking public spaces and green areas.
This public space becomes the meeting point and an intimious place for the inhabitants in order to achieve relations among the inhabitans and ensure a closer community feeling.
The Building
These units represent the evolution of the plan, the continuity of the ground plan.
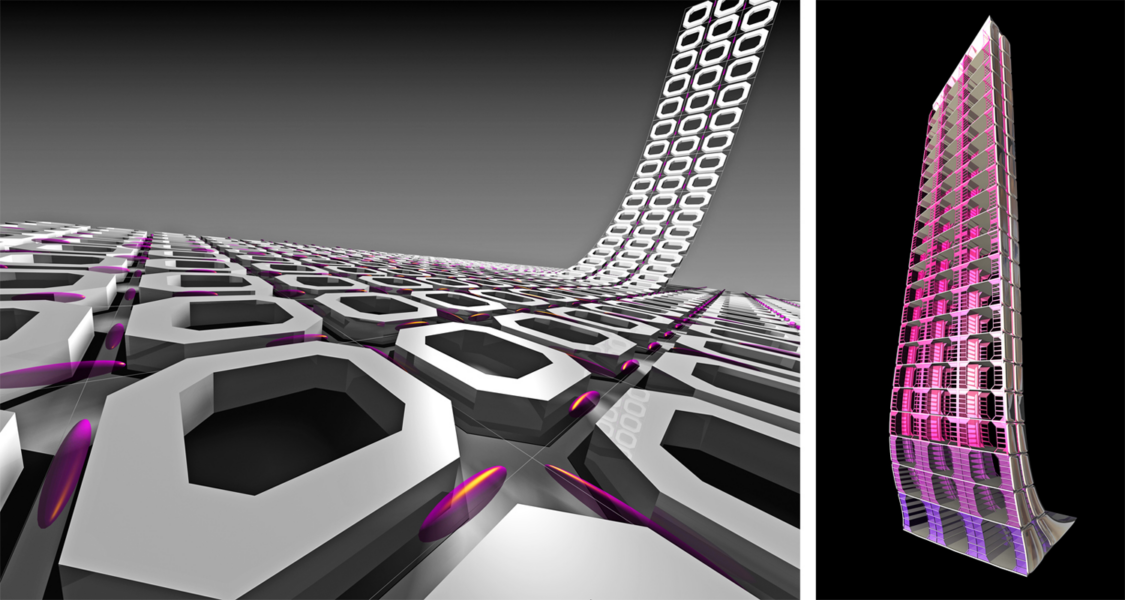
The building as a spine is made by the aggregation of the unit block add to each other, the generative process is based on fluid dynamics forces as a potential strategy to organize infrastructural flows and social formations, establishing a coherent relationship between building system and the surrounding.
The building becomes a social and economical pole attraction in an area already in expansion. From the big scale to the small scale. The development of the Skyscraper is not a layered sovrappoition of planes and floors but is an addiction of units that can be done to the infinity.
The building capture the (dynamics) of the site in several ways, spatially, organizationally and by means of its system of enclosure fusing into an hyphenated formation. The parametric matrix of the internal spatial organization breaking down the typologically system based on layered floors.
Parametres that define individual units and involve the relationship between interior and exterior spaces, floating from the big to the human and intimious scale.
A parametric building is constructed from a spline that develop the grid from the urban field, amplify the urban vectors in a generative vertical shape that informs forces and shaping the building.
Sustainability
The building is formed in a way to consider the social environmental aspects.
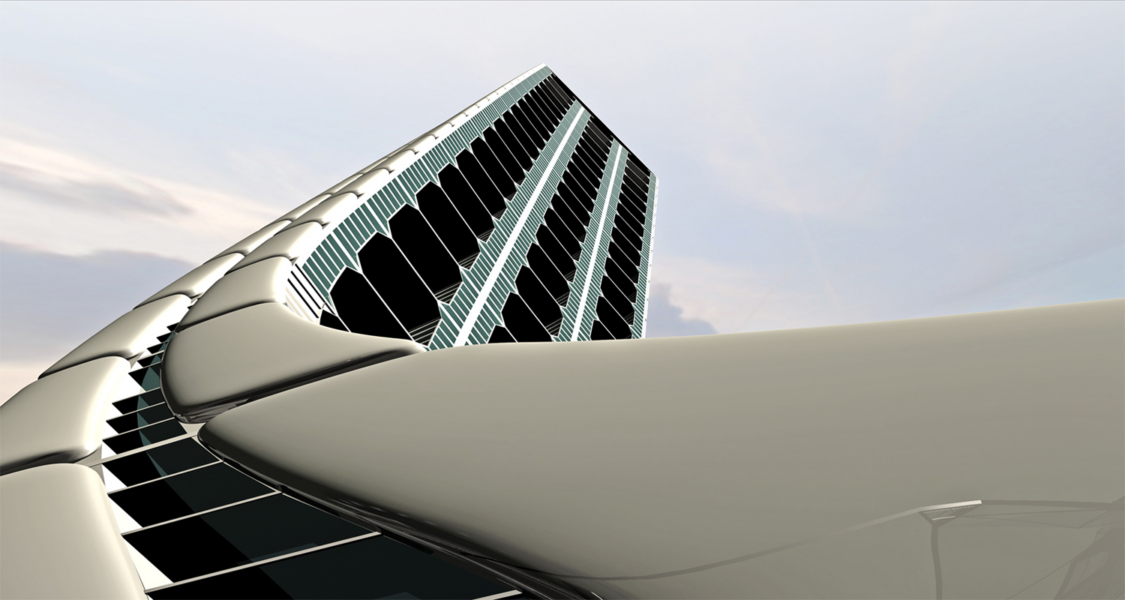
The torsion follows the sun given maximum exposure to the light.
Gardens/ daylight/ natural ventilation/energy conservation system/ water capture-recycling-collective water/photovoltaic cells in the residences windows.